Periodontal probe
Assessment instruments
Periodontal probe
The periodontal probe is a rod-shaped instrument with blunt tip used for assessment of the periodontal and peri-implant tissues. There are various types of probe designs and millimeter markings.
Findings from an assessment with a periodontal probe are an important part of a comprehensive periodontal assessment.
The calibrated periodontal probe is used to:
- Survey probing depths (PD) around teeth or implants
- Evaluate for presence of bleeding or suppuration (BOP/SUP)
- Determine the position of the gingival margin
- Measures clinical attachment loss (CAL)
- Determine the width of keratinized tissue/gingiva
- Measure width and length of oral deviations or lesions such as lumps, ulcers, etc.
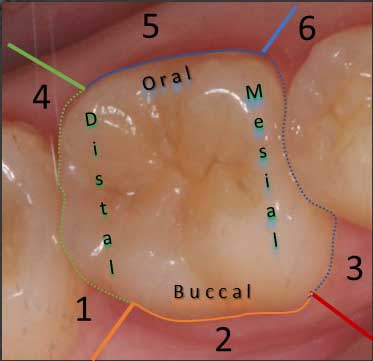
How to record readings on the periodontal chart?
For purposes of assessment, each tooth is divided into six sites. Readings are recorded at six sites per tooth: three readings on the buccal and three on the oral aspect of the tooth. If the tissue contacts the probe halfway between millimeter marks, the reading should be rounded up to the higher millimeter reading. For example, if the reading is at 6.5mm, it should be recorded as 7mm.
The probe is “walked” around the tooth using a gentle probing force and only the highest measurement is recorded per site.
Periodontal probe